




Next: 3 Spectrograph Control
Up: Part II: Subsystem Designs
Previous: 1 Slitmask Design &
This subsystem is used to acquire a field and align a slitmask
with respect to the sky. In practice, field acquisition is performed by
the Observing Assistant, using standard DCS commands to place user-supplied
coordinates at a desired pointing origin.
Therefore, the subsystem description here will focus primarily on the
mask-alignment process, although one of the modules is
useful for precise relative positioning for any purpose.
The modules described are XLATE and SMALIGN.
There is a dependency on the mask-design (database), specifically with the
slitmask initialization procedure (see 2.5).
See Figure 2.1, ``Mask Alignment Flow.''
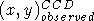
Figure 2.1: Mask Alignment Flow
- Alignment Star:
- Preselected star or other object to be centered
in an alignment box.
- Alignment Box:
- Small rectangular aperture on slitmask,
in which alignment star is centered when the mask is properly aligned.
- Guide Star:
- Preselected star or other object to be placed at a
particular location on the TV, either for object acquisition or guiding.
- Database Extract:
- A file on the local disk containing slitmask designs,
extracted from the database by the slitmask initialization process.
- Function
- Calculate and apply telescope offset to translate
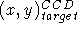 to
to 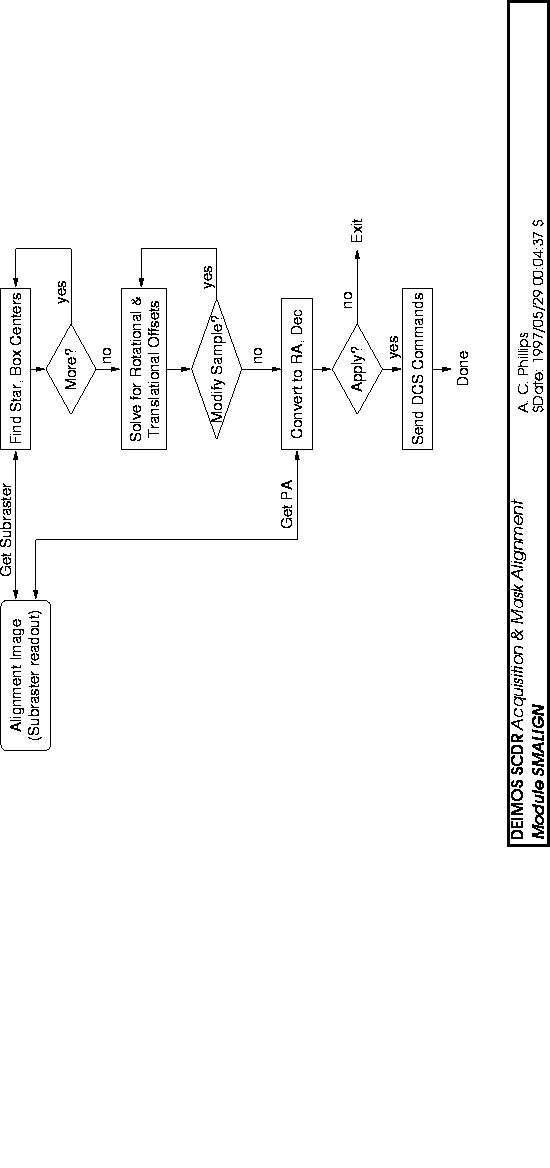 .
.
- Language
- IRAF/spp
- Type
- tool
- Author
- A. C. Phillips
- Revision
- N/A
- Essay
-
This basic module takes an input (x,y) in CCD pixels (``observed'' coordinates),
and an instrumental position angle and target (x,y) in pixels, and calculates
the necessary telescope offset in arcseconds to translate from the observed
to target locations.
The user is queried for permission to apply these offsets, and DCS commands
are issued upon confirmation.
For mask alignment, the observed coordinates are those of an alignment star,
and the target coordinates those of the corresponding alignment box.
In practice, the positioning of the guide star at its predicted TV coordinates
should be accurate enough that XLATE will not be required.
The source of the input parameters (input and target coords, PA) may vary.
For example, the input (x,y) may be selected by mouse-click on the image
display, the PA taken from the image header, and the target coordinates
preselected from the database extract. Another source for input (x,y) might
be a centroiding routine. Initially, we will provide only the
simple interface - that is, the user enters all parameters by hand.
This module duplicates the functionality of modifying DCS keywords
INSTXOFF and INSTYOFF, but is provided as an easier means for the observer
to achieve the desired moves.
- Inputs
- observed/target CCD coord pairs; PA of observation
- Outputs
- printed telescope offsets; DCS commands
- Deployment
- Commissioning
- Labor
- 20 hours
- Keywords used by module
-
Modifies DCS keywords: RAOFF, DECOFF, REL2CURR
Waits on DCS keywords: AXESTAT
Define the offsets between the telescope axis and the pointing
origins for the slitmask, longslit, imaging field and TV centers.
Calibrate the actual slitmask-to-TV coordinate system mapping.
Calibrate the Position Angle zeropoint of the instrument to within
about 0.1 degree (preferably much better than this).
Instrument Specialist loads the slitmasks in the instrument. Then,
either the observer or instrument specialist selects the ``initialize''
option on the instrument GUI (Part I, Chapter  ).
This causes the system to cycle
through the loaded slitmasks, scanning barcodes and querying the database for
the slitmask design associated with each mask. The slitmask info is placed
on a local disk so that operation during the night does not depend
on the availability of the database.
).
This causes the system to cycle
through the loaded slitmasks, scanning barcodes and querying the database for
the slitmask design associated with each mask. The slitmask info is placed
on a local disk so that operation during the night does not depend
on the availability of the database.
Expected Mode:
- 1.
- OA acquires field, sets instrument PA
- 2.
- Insert slitmask
- 3.
- Translate to place guide star at its expected TV location
- 4.
- Execute module SMALIGN
Fallback Mode (if placement of Guide star at expected TV coordinates
fails to put the alignment stars within their boxes):
- 1.
- OA acquires field, sets instrument PA
- 2.
- Take direct image
- 3.
- Examine image to get alignment star coordinates
- 4.
- Execute module XLATE
- 5.
- Insert Slitmask
- 6.
- Execute module SMALIGN
Instructions for the mask alignment procedure will be provided. These should
be available in on-line form. Also, module SMALIGN will include
built-in on-line help (eg., list of commands; sketch of normal operations; some
troubleshooting).





Next: 3 Spectrograph Control
Up: Part II: Subsystem Designs
Previous: 1 Slitmask Design &
DEIMOS Software Team <deimos@ucolick.org>
1997-06-13T00:18:19
 .
.
![]() ).
This causes the system to cycle
through the loaded slitmasks, scanning barcodes and querying the database for
the slitmask design associated with each mask. The slitmask info is placed
on a local disk so that operation during the night does not depend
on the availability of the database.
).
This causes the system to cycle
through the loaded slitmasks, scanning barcodes and querying the database for
the slitmask design associated with each mask. The slitmask info is placed
on a local disk so that operation during the night does not depend
on the availability of the database.