




Next: 6 CCDs - Procedures
Up: Part III: DEIMOS Calibration:
Previous: 4 Overview of Data
Prior to and during commissioning, various calibrations must be performed
before the instrument is ready to produce science data that can be
readily interpreted. These calibrations concern the geometrical mappings
between coordinate systems described in Chapter 2. They are:
- Slitmask Astrometry, or mapping the sky (RSCS) onto the slitmask (SMCS);
- TV Astrometry, or mapping the sky (RSCS) onto the TV system (TVCS); and
- CCD alignment, or measuring the rotations and translations of the
individual CCDs in the mosaic (CCDCSi) relative to the Image Coordinate
System (ICS).
This does not describe all mappings. Certain mappings
(FKCS to RSCS) are handled purely through modelling. Others will be
handled during observing (SMCS to MFCS) or determined empirically
during science calibrations (SM/MFCS to ICS; ICS to RSCS).
(nothing major)
The slitmask astrometry mapping will be maintained in the database.
The TV astrometry mapping will be maintained in the database.
The CCDCSi 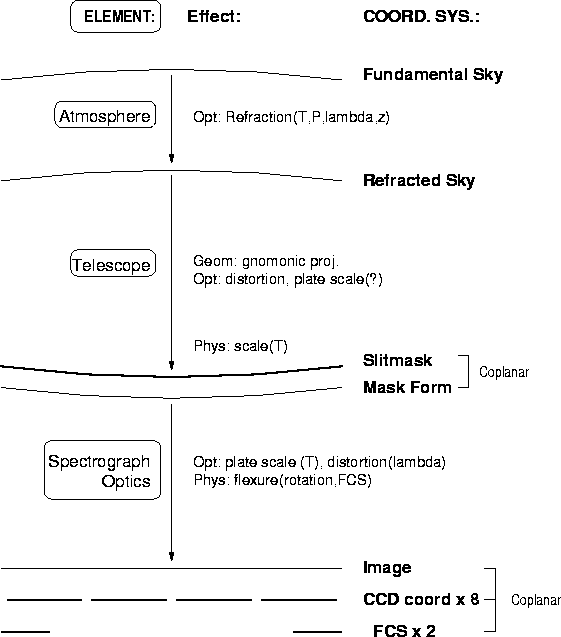 ICS mapping will be maintained in the database.
ICS mapping will be maintained in the database.
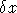
NOTES -- Delivery: 0=Commissioning, 1=Pipeline.
Required Hardware:
- -
- Mask form fiducial marks
- -
- Slitmask of astrometric field, based on expected projections.
- -
- Grid-of-holes (GOH) mask
- -
- Line-of-holes (LOH) mask
- 1.
- Select astrometric field; prepare a slitmask using existing
slitmask mapping (pure model initially). This slitmask will have small
pinholes at the expected position of selected stars.
- 2.
- Align mask with the selected field; take one or more images of
the mask.
- 3.
- Remove mask; take one or more images of the field; process all images
through relative flux calibration.
- 4.
- Measure the pixel positions of each selected star and its
corresponding pinhole.
- 5.
-
Convert the differences between each coordinate pair into mm on the slitmask.
(Detailed mapping not necessary in this conversion.)
Fit the mm offsets as a function of slitmask location. This becomes the
differential update to the slitmask astrometry model.
- 1.
- Take TV exposure showing mask form fiducials and fixed mirror.
- 2.
- Analyse location of maskform fiducials to solve for scale, rotation
and translation of TVCS wrt MFCS.
- 3.
- Use slitmask astrometry mapping to relate this to the refracted sky.
- 4.
- Mapping can be verified against an astrometric field.
Note: the above assumes negligible distortion in the TV camera. If this is not
valid, observations of astrometric fields must be used to map out the
distortion. The level of distortion can be tested (pre-commissioning)
in the lab, using the image of a grid-of-holes mask. The level of telescope
distortion (also a potential factor) is ?? (negligible) over the FOV of the
TV.
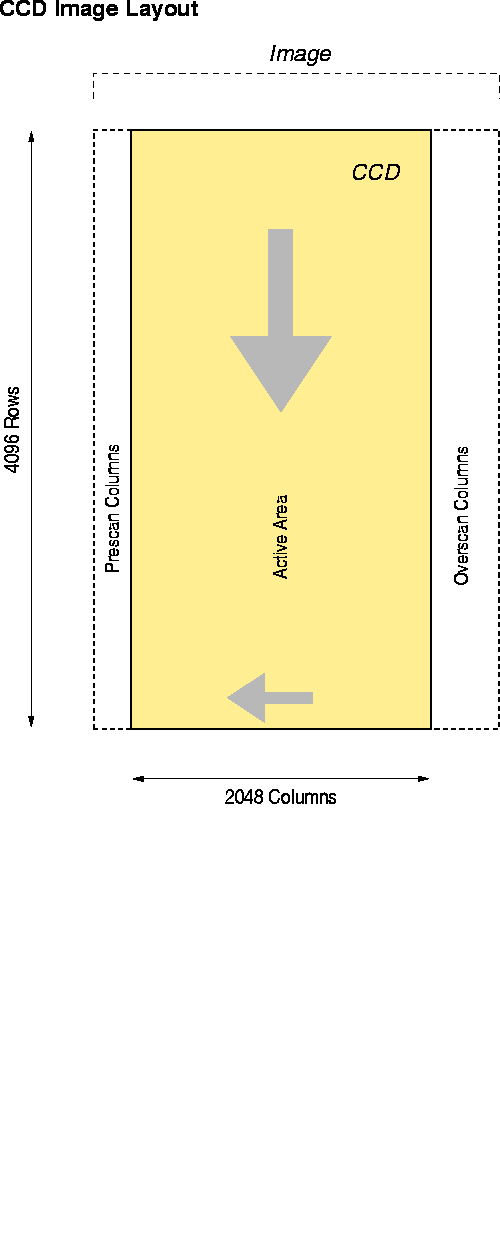
- 1.
- Take a direct image (no slitmask) of flat field. Measure the
location of the mask form fiducials. Using the known location of the
fiducials wrt the telescope/collimator optical axis, solve for the
rotation, scale and approximate zeropoint offsets for the fiducial CCD.
- 2.
- Take a flat field image through the grid-of-hole (GOH) mask.
Measure the locations of the holes on each mask and solve for a rotation
and translation relative to the fiducial CCD. Convert to ICS using the
transformation above.
- 3.
- Take a spectral flat-field exposure through the line-of-holes (LOH)
mask. Measure the spectral traces across the CCDs. The change in
slope
 characterizes the red vs blue CCD rotation. This rotation can be related to
the fiducial CCD and thus the ICS.
characterizes the red vs blue CCD rotation. This rotation can be related to
the fiducial CCD and thus the ICS.
- 4.
- Take a spectral arc exposure through the line-of-holes (LOH)
mask. Using the traces above, locate and measure the emission line (spots) in
the spectrum from each hole.
These may be used to determine a
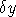 ,
,  across each CCD boundary.
In conjunction with the angle, these deltas provide the translations for
the red CCD relative to the blue CCDs, which in turn are known relative
to the ICS.
across each CCD boundary.
In conjunction with the angle, these deltas provide the translations for
the red CCD relative to the blue CCDs, which in turn are known relative
to the ICS.
We have not addressed the FCCSj yet.





Next: 6 CCDs - Procedures
Up: Part III: DEIMOS Calibration:
Previous: 4 Overview of Data
DEIMOS Software Team <deimos@ucolick.org>
1997-06-13T00:18:19
 ICS mapping will be maintained in the database.
ICS mapping will be maintained in the database.
 ICS mapping will be maintained in the database.
ICS mapping will be maintained in the database.
![]()
 across each CCD boundary.
In conjunction with the angle, these deltas provide the translations for
the red CCD relative to the blue CCDs, which in turn are known relative
to the ICS.
across each CCD boundary.
In conjunction with the angle, these deltas provide the translations for
the red CCD relative to the blue CCDs, which in turn are known relative
to the ICS.